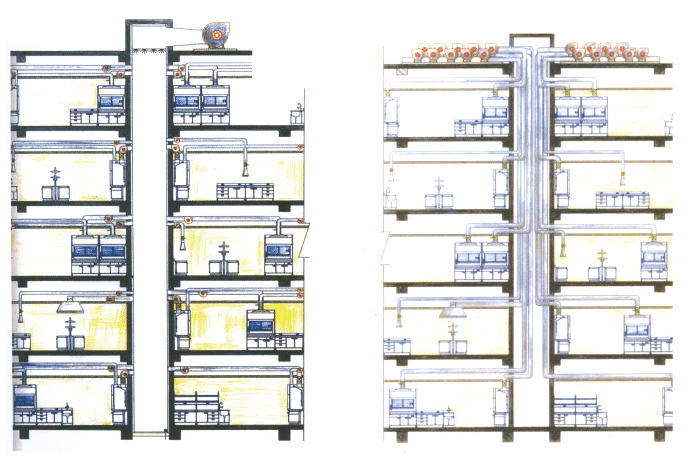
Laboratory ventilation system
Laboratory ventilation control system
There are two types of exhaust systems for fume hoods: one is constant type (CV, Constant airvolume), and the other is variable type (VAV, Varible air volume). Both exhaust modes can be operated in separate fume hoods or in multiple fume hood systems with exhaust manifolds. At the same time, the exhaust system of the fume hood needs to be compatible with the indoor air conditioning system.
Due to the complexity and particularity of the laboratory, the design of the laboratory ventilation system is different from the ventilation design requirements of the comfort air conditioning system. The main purpose of the laboratory ventilation design is to provide a safe and comfortable working environment and reduce indoor air pollution. Ventilation mainly solves the problem of the physical health and labor protection of the working environment for the staff. To ensure the safety of the experimental personnel, in addition to the problem of the position and number of the fume hood, the core problem is to ensure that the surface wind speed of the fume hood is constant within the safe range. The general standard is (0.5-0.1) m/s. This requires a sensor variable air volume control system at the regulating valve of the fume hood. To ensure that the ventilation air volume of the fume hood reaches a given surface wind speed. The variable air volume system has obvious advantages: good safety. High surface wind speed (0.5m/s) can be achieved when the operator has disturbance behavior in front of the fume hood: when the operator is absent, a safe surface wind speed (0.3m/) that guarantees that the harmful substances are not leaked can be used. s). Reduce airflow while ensuring a safe and comfortable working environment. Energy savings have been achieved. Since most of the time is operated under low flow conditions, the system noise is low; the system reacts quickly, ensuring the dust collecting capacity of the fume hood.